Abstract Factory Pattern in TypeScript
The Abstract Factory Pattern is a creational design pattern that lets you produce families of related objects without specifying their concrete classes. Think of it as a “factory of factories”—a higher-level abstraction that creates other factories, which in turn create objects.
In TypeScript, this pattern is particularly powerful because of its strong typing system, which helps enforce relationships between families of objects at compile time.
Visual Aid: Abstract Factory Overview
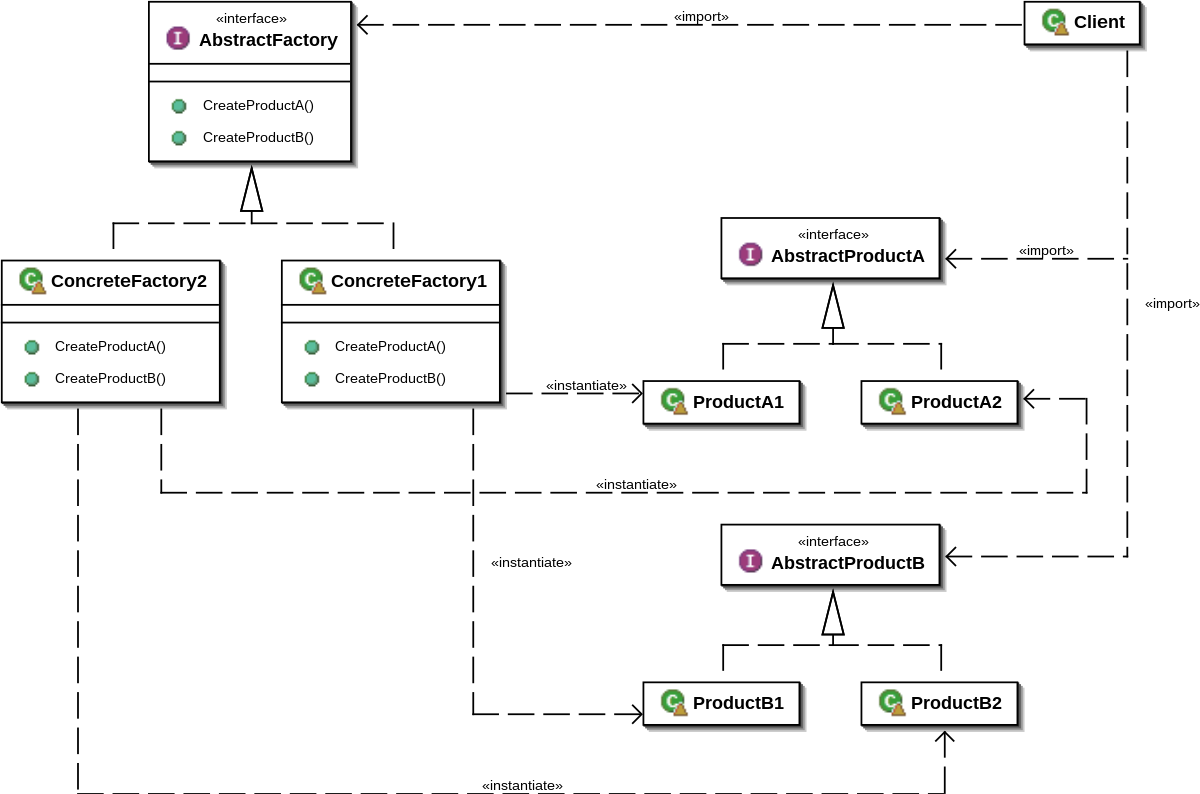
Source: wikipedia
🔹 Why It Matters
Imagine you’re building a UI framework that supports multiple themes (e.g., Light and Dark). Each theme has its own set of components (buttons, checkboxes, etc.) with different styles. The Abstract Factory Pattern allows you to:
- Encapsulate object creation for each theme.
- Ensure consistency—all components in a family (e.g., Light theme) are compatible.
- Swap families easily without changing client code.
This is crucial in large applications where you need to manage complex object hierarchies or support multiple platforms/themes.
🔹 Core Concepts
Key Components:
- Abstract Factory: Declares an interface for creating abstract products.
- Concrete Factories: Implement the factory interface to create concrete products.
- Abstract Products: Define interfaces for the products being created.
- Concrete Products: Implement the abstract product interfaces.
Real-World Use Case:
A cross-platform UI library where you need to create platform-specific components (e.g., WindowsButton, MacOSButton).
🔹 Code Walkthrough
Let’s implement a simple example: a UI factory for Light and Dark themes.
Step 1: Define Abstract Products
// Abstract Product: Button
interface Button {
render(): string;
}
// Abstract Product: Checkbox
interface Checkbox {
render(): string;
}Step 2: Define Concrete Products
// Concrete Product: Light Theme Button
class LightButton implements Button {
render(): string {
return '<button style="background: white; color: black;">Light Button</button>';
}
}
// Concrete Product: Dark Theme Button
class DarkButton implements Button {
render(): string {
return '<button style="background: black; color: white;">Dark Button</button>';
}
}
// Concrete Product: Light Theme Checkbox
class LightCheckbox implements Checkbox {
render(): string {
return '<input type="checkbox" style="accent-color: black;">';
}
}
// Concrete Product: Dark Theme Checkbox
class DarkCheckbox implements Checkbox {
render(): string {
return '<input type="checkbox" style="accent-color: white;">';
}
}Step 3: Define Abstract Factory
// Abstract Factory
interface UIFactory {
createButton(): Button;
createCheckbox(): Checkbox;
}Step 4: Define Concrete Factories
// Concrete Factory: Light Theme Factory
class LightUIFactory implements UIFactory {
createButton(): Button {
return new LightButton();
}
createCheckbox(): Checkbox {
return new LightCheckbox();
}
}
// Concrete Factory: Dark Theme Factory
class DarkUIFactory implements UIFactory {
createButton(): Button {
return new DarkButton();
}
createCheckbox(): Checkbox {
return new DarkCheckbox();
}
}Step 5: Client Code
// Client code that uses the factory
function renderUI(factory: UIFactory) {
const button = factory.createButton();
const checkbox = factory.createCheckbox();
console.log(button.render());
console.log(checkbox.render());
}
// Usage
console.log("Light Theme:");
renderUI(new LightUIFactory());
console.log("\nDark Theme:");
renderUI(new DarkUIFactory());Output:
Light Theme:
<button style="background: white; color: black;">Light Button</button>
<input type="checkbox" style="accent-color: black;">
Dark Theme:
<button style="background: black; color: white;">Dark Button</button>
<input type="checkbox" style="accent-color: white;">🔹 Common Mistakes
- Overcomplicating Simple Scenarios: If you only need one type of object, use the simpler Factory Method Pattern instead.
- Tight Coupling: Ensure factories are independent of concrete product classes.
- Ignoring TypeScript Benefits: Leverage interfaces and generics to enforce type safety.
🔹 Best Practices
- Use Dependency Injection: Pass factories as dependencies to make testing easier.
- Combine with Dependency Inversion Principle: Depend on abstractions, not implementations.
- Document Families Clearly: Ensure it’s obvious which products belong to which families.
🔹 Final Thoughts
The Abstract Factory Pattern is a powerful tool for managing complex object creation, especially in applications with multiple families of related objects. In TypeScript, its strong typing system makes it even more robust, helping catch errors at compile time.
For further reading: